How French Can Help You Immigrate to Canada More Easily
- February 21, 2024
- 5 min

Introduction:
Canada's multicultural ethos and bilingual nature offer a distinct advantage to those proficient in both of its official languages: English and French. This article delves into the myriad ways in which French language proficiency can significantly ease the immigration process to Canada. From enhancing your points in immigration programs to facilitating cultural integration and expanding employment opportunities, speaking French can be a crucial asset in your Canadian immigration journey.
The Importance of Bilingualism in Canadian Immigration:
In the realm of Canadian immigration, bilingualism is a prized asset, particularly emphasized in the Express Entry system and Provincial Nominee Programs (PNPs). In the Express Entry system, candidates are assessed under the Comprehensive Ranking System (CRS), where additional points are awarded for proficiency in a second official language. French-speaking candidates can gain up to 30 additional CRS points, which can be pivotal in receiving an invitation to apply for permanent residence. Similarly, PNPs often favor candidates with French language skills, especially in regions with significant Francophone populations. For instance, Ontario's French-Speaking Skilled Worker Stream is specifically designed for French-speaking skilled workers who want to live and work in Ontario.
French: A Gateway to Quebec and Other Francophone Communities:
Quebec, with its unique cultural identity and language, runs its own immigration programs, such as the Quebec Skilled Worker Program (QSWP). Proficiency in French is not just an asset but often a requirement for these programs. Quebec's immigration process awards significant points for French language skills, making it an attractive option for French-speaking immigrants. Furthermore, Canada is home to vibrant Francophone communities outside Quebec, such as in New Brunswick and parts of Ontario. French proficiency can facilitate smoother integration into these communities, allowing immigrants to connect more deeply with their local culture and society.
Employment Opportunities for French Speakers:
Canada's job market heavily favors bilingual candidates, particularly in sectors such as government, education, and business. Federal government positions often require proficiency in both official languages. In education, teachers and administrators with French skills are in demand in French immersion schools and bilingual provinces. Moreover, global corporations in Canada frequently seek bilingual employees to serve both English and French-speaking markets. Fluency in French can lead to more competitive salaries and a broader range of career opportunities across the country.
Cultural Integration and Social Benefits:
Mastering French not only aids in navigating the Canadian immigration process but also enriches the cultural and social experience. Being able to communicate in French opens doors to a richer interaction with Canada's diverse communities. It allows for a deeper appreciation of the country's Francophone heritage, festivals, and arts. Additionally, speaking French can foster a sense of belonging and community, especially in Francophone regions, easing the often challenging transition of adapting to a new country.
Success Stories and Testimonials:
The impact of French proficiency on Canadian immigration is best illustrated through personal stories. Many immigrants have shared their experiences of how French language skills have facilitated their journey, from scoring higher in immigration programs to securing their dream job in Canada. These testimonials highlight the tangible benefits of bilingualism in real-life scenarios, serving as inspiration for potential immigrants.
French Language Learning Resources for Immigrants:
Acknowledging the importance of French, numerous resources are available for immigrants to learn or improve their language skills. These include government-funded language classes, online courses, community language groups, and cultural immersion programs, all designed to support non-French speakers in their quest to become bilingual.
Increase your probability of receiving invitation by Learning French:
Recently, there has been a notable increase in the number of people who find learning French easier and more accessible, significantly aiding their efforts to migrate to Canada. This trend is attributed to the comprehensive resources available for French language learning, tailored specifically for immigration purposes. Canada, with its significant Francophone population, particularly values French language proficiency, often making it a favorable factor in immigration applications. As a result, individuals who have mastered French are finding it relatively smoother to receive invitations for Canadian immigration, opening up opportunities for them in a country known for its cultural diversity and inclusive policies.
TEF & DELF:
The TEF (Test d'Évaluation de Français) and DELF (Diplôme d'Études en Langue Française) are two different French language proficiency tests recognized for immigration and other purposes in Canada.
TEF (Test d'Évaluation de Français):
Purpose: The TEF is designed to assess the level of French language proficiency for non-native speakers. It is often used for Canadian immigration purposes, especially for those applying through economic immigration programs like the Quebec Skilled Worker Program.
Components: It evaluates reading, writing, listening, and speaking skills.
Scoring: The TEF uses a scoring system that is aligned with the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR). Scores are given for each component, and there's an overall score as well.
DELF (Diplôme d'Études en Langue Française):
Purpose: The DELF is a certification of French-language abilities for non-native speakers. It's recognized by the French Ministry of Education and is also accepted for Canadian immigration purposes.
Components: Like the TEF, it assesses reading, writing, listening, and speaking skills.
Levels: The DELF is divided into four independent diplomas corresponding to the CEFR levels: A1, A2, B1, and B2. Beyond these, there's the DALF, covering C1 and C2 levels.
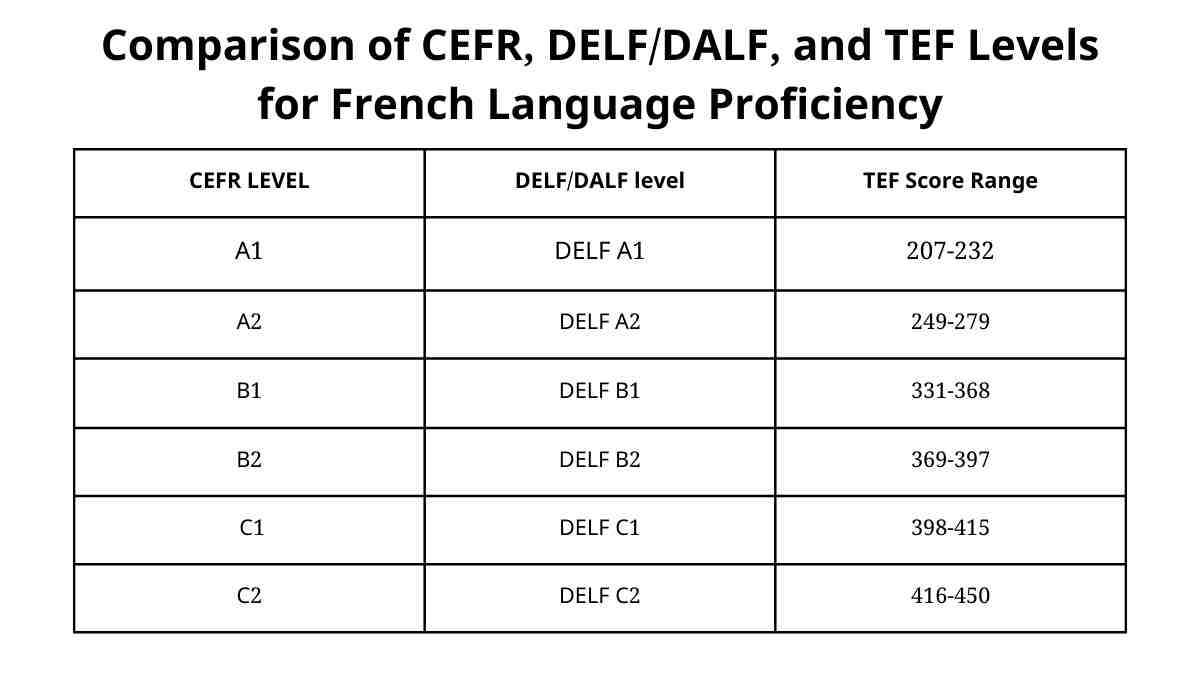
Both TEF and DELF/DALF are aligned with the CEFR, which provides a basis for comparing language proficiency levels. CEFR levels range from A1 (beginner) to C2 (advanced).
Here is a chart that showcases the relationship between the CEFR levels, DELF/DALF levels, and TEF score ranges:
CEFR Level: Indicates the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages level, ranging from A1 (beginner) to C2 (advanced).
DELF/DALF Level: Corresponding levels for the DELF (A1 to B2) and DALF (C1 to C2) exams.
TEF Score Range: The score range for each CEFR level as assessed by the TEF.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, French language proficiency offers a strategic advantage in the Canadian immigration process. From increasing points in immigration programs to enhancing employment prospects and facilitating cultural integration, French can be a key to unlocking a successful Canadian immigration experience. For those considering a move to Canada, investing time in learning French can significantly boost your chances of a smooth transition and a fulfilling life in this beautifully diverse country.