Navigating the Skilled Occupation List: A Gateway to Australian Immigration and Citizenship
- February 23, 2024
- 5 min

Introduction
In the realm of global mobility and immigration, Australia stands out as a prime destination for skilled professionals seeking new opportunities. Central to this process is the Australian Skilled Occupation List (SOL), a dynamic and strategic tool used by the Australian government to align foreign skilled labor with the nation's economic needs. This article delves into the intricacies of the SOL, examining its role, impact, and implications for immigration and citizenship in Australia.
Understanding the Skilled Occupation List
The Skilled Occupation List is a curated compilation of professions deemed essential for Australia's workforce. The primary objective of the SOL is to address skill shortages in the Australian labor market by attracting foreign professionals with the expertise and experience in these listed occupations. These occupations are meticulously selected based on extensive labor market research and economic forecasting, ensuring that the list reflects the evolving needs of the Australian economy.
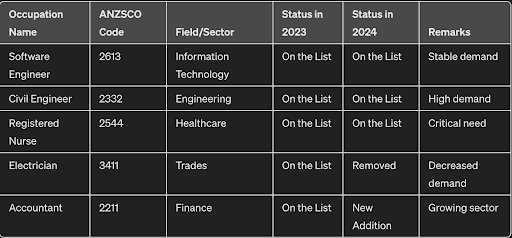
One hypothetical example of the sheet would be as it looks below:
Criteria for Inclusion in the Skilled Occupation List
The process of determining which occupations make it onto the SOL is comprehensive and data-driven. It involves analysis of labor market trends, consultation with industry leaders, and consideration of factors such as the rate of unemployment in certain sectors, the future growth potential of industries, and the need for specific skills in the Australian market. Occupations on the SOL are reviewed regularly to ensure relevance and responsiveness to the changing economic landscape.
This list is pivotal in Australia's immigration policy, particularly for skilled migration visas. The occupations included in this list are selected based on their perceived importance to the Australian economy and the current labor market needs. The criteria for inclusion are multifaceted and involve extensive analysis and consultation.
Labor Market Needs:
The primary factor for an occupation's inclusion in the SOL is the demand for that skill in the Australian labor market. This involves analyzing employment trends, vacancy rates, and the expected future demand for certain skills. The government identifies sectors with skill shortages and includes occupations within these sectors on the list.
Economic Contribution and Sustainability:
Occupations that significantly contribute to Australia's economic growth are prioritized. The sustainability of the occupation in terms of long-term relevance to the Australian economy is also a key consideration.
Consultation with Industry Bodies:
The Australian government consults with various industry bodies, employers, unions, and professional organizations to gather insights about the skill needs in different sectors. These consultations help in identifying specific roles that are in short supply.
Analysis of Training and Education Pathways:
The government examines the availability of educational and training pathways in Australia for each occupation. Occupations that require skills which are not readily available or trainable within Australia are more likely to be included on the SOL.
National and Regional Needs:
The list takes into account both national and regional skill shortages. Some occupations are included specifically to address regional shortages and may appear on the Regional Occupation List (ROL) or other similar lists.
Public and Stakeholder Submissions:
Submissions from the public and stakeholders, which can include businesses, educational institutions, and local communities, are considered. These submissions provide grassroots-level insights into the actual skill needs and shortages across different regions and sectors.
International Comparisons and Agreements:
Australia may include certain occupations on the SOL to align with international agreements or to maintain competitiveness in attracting global talent.
Data Analysis and Research:
Extensive data analysis and research underpin the selection process. This includes labor market research, economic forecasts, and analysis of census and employment data. Government departments like the Department of Jobs and Small Business play a key role in this research.
Regular Review and Update:
The SOL is not static; it is regularly reviewed and updated to reflect the changing needs of the Australian economy and labor market. This ensures that the list remains responsive and relevant. The criteria for inclusion in Australia's Skilled Occupation List are comprehensive and designed to ensure that the country’s immigration policy is closely aligned with its economic and labor market needs. By selecting occupations based on these criteria, Australia aims to address skill shortages effectively and foster economic growth.
Impact on Immigration Policies
VThe SOL significantly influences Australia's immigration policy. It is a cornerstone of various visa programs, including the Skilled Independent Visa (subclass 189), Skilled Nominated Visa (subclass 190), and the Temporary Skill Shortage Visa (subclass 482). These visas allow individuals with skills listed on the SOL to apply for residency, and potentially citizenship, in Australia. This alignment of immigration policy with the labor market ensures that the influx of skilled migrants contributes positively to the country's economic growth and social fabric.
Case Studies: Occupations on the Australian Skilled Occupation List
Illustrating the diversity of the SOL, occupations range from healthcare (such as nurses and doctors) to engineering (like civil and mechanical engineers), IT specialists, and tradespeople (including electricians and carpenters). Each of these professions plays a critical role in sustaining key sectors of the Australian economy.
Benefits of the Skilled Occupation List
The SOL offers a win-win scenario for both Australia and skilled immigrants. For Australia, it addresses labor shortages, drives economic growth, and ensures a competitive edge in the global market. For immigrants, it opens up pathways for career advancement, stable employment, and an opportunity to become permanent residents or citizens in a country known for its high quality of life and robust economy.
Challenges and Criticisms
Despite its advantages, the SOL is not without challenges. Critics argue that it may not always accurately reflect real-time labor market needs due to its periodic review process. There's also the concern that it may prioritize certain skills over others, potentially overlooking emerging industries or non-traditional roles. Moreover, navigating the visa application process linked to the SOL can be complex and daunting for potential immigrants.
The Future of the Skilled Occupation List
Looking ahead, the SOL is expected to evolve in response to global trends, such as technological advancements and the changing nature of work. It might see a greater emphasis on digital skills, renewable energy technologies, and healthcare expertise, especially in the wake of global challenges like the COVID-19 pandemic.
Conclusion
The Australian Skilled Occupation List is a testament to the country's strategic approach to immigration and citizenship. By aligning immigration with economic needs, Australia not only enriches its labor market but also offers a promising future to skilled professionals worldwide. As global dynamics shift, the SOL will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping Australia's workforce and its position on the world stage.